Introduction
In the demanding world of material handling and heavy industry, efficiency, safety, and robust performance are non-negotiable. The Double Girder Gantry Crane stands as a cornerstone of these operations, offering unparalleled strength and versatility for lifting extremely heavy loads across vast spans. From shipyards and manufacturing plants to construction sites and logistics hubs, these cranes are engineered to handle the toughest tasks. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about double girder gantry cranes—from their fundamental design and advantages to applications, key considerations, and the latest technological advancements.
What is a Double Girder Gantry Crane?
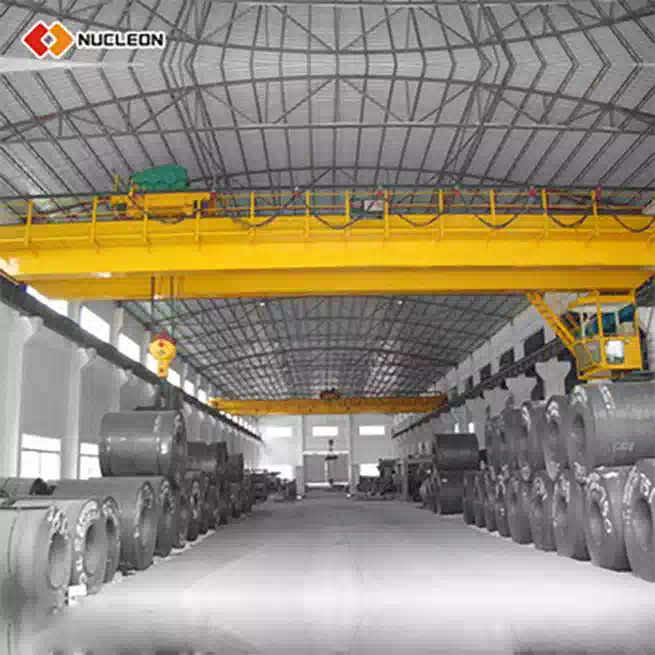
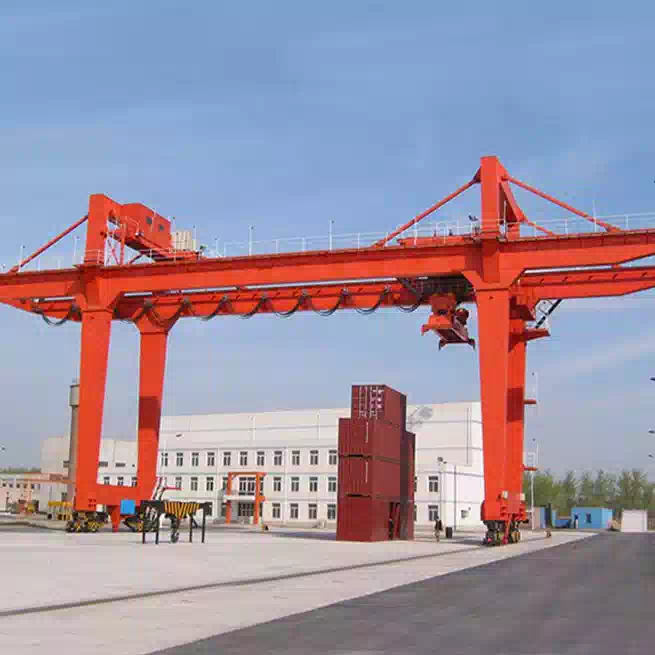
A Double Girder Gantry Crane is an overhead lifting system characterized by two primary bridge girders that run parallel to each other, mounted on top of a gantry structure with legs that travel on fixed rails or wheels. The hoist trolley moves along the top of these two girders, providing exceptional stability and a higher hook height compared to single girder designs. This configuration is designed for heavy-duty applications, typically handling loads from 20 tons up to several hundred tons, with spans often exceeding 30 meters.

Key Components:
Bridge Girders: The main horizontal beams that form the crane's bridge, supporting the trolley and the load.
End Trucks: Structures at each end of the girders, housing the wheels and drive mechanisms for longitudinal movement along the runway rails.
Hoist Trolley: The unit that travels across the bridge girders, containing the hoist (motor, drum, rope/chain), hook, and its own drive system.
Legs/Frames: Upright support structures that transfer the load to the ground or foundation, often equipped with wheels for mobility.
Runway System: The rails or track on which the entire gantry crane travels.
Control System: Includes the operator's cabin (mounted on the trolley or suspended), radio remote control, and all electrical panels.
Key Advantages of Choosing a Double Girder Design
Opting for a double girder gantry crane brings significant benefits for heavy-lift scenarios:
Higher Lifting Capacity & Hook Height: The dual-girder design provides a stronger structural framework, allowing for greater lifting capacities. Crucially, the hoist trolley is mounted on top of the girders, not suspended beneath them. This maximizes the hook lift height—the vertical distance between the rail and the hook—making it ideal for lifting tall loads or working in facilities with high ceilings.
Superior Structural Integrity & Stability: The two girders distribute the load more evenly, minimizing deflection (sagging) under heavy loads. This results in smoother, more precise load movement and reduced wear on components, leading to a longer service life.
Enhanced Versatility & Customization: The spacious area between and on top of the girders easily accommodates additional equipment. This includes:
Auxiliary Hoists for lighter, secondary lifts.
Specialized Lifting Attachments like magnets, grabs, or vacuum lifters.
Maintenance Walkways and platforms for safe and easy access.
Improved Trolley Performance: The trolley running on top of wide-flanged rails offers better traction and alignment, leading to smoother travel, reduced wheel wear, and the ability to handle more severe duty cycles.
Long-Term Durability & Lower Lifetime Cost: While the initial investment is typically higher than a single girder crane, the enhanced durability, reduced maintenance needs, and higher productivity often result in a better total cost of ownership (TCO) for demanding applications.
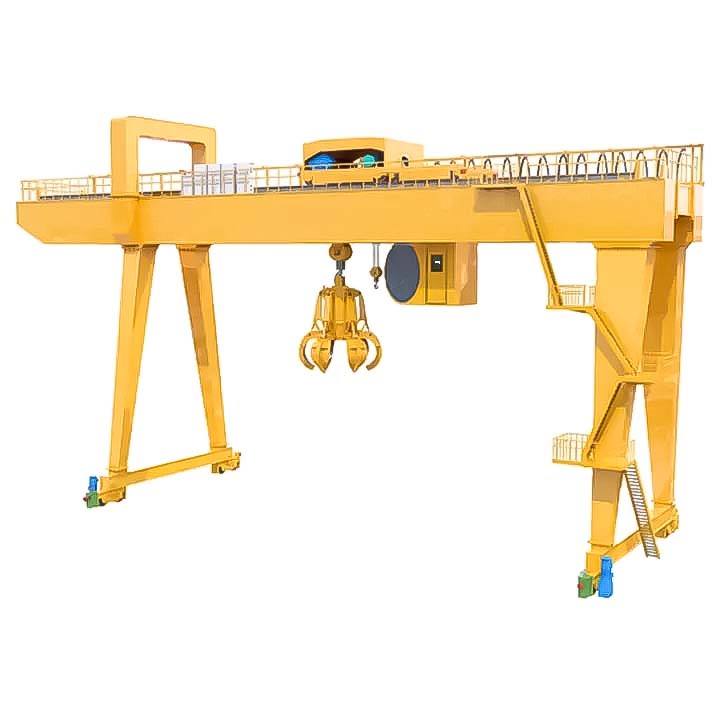

Applications: Where Are Double Girder Gantry Cranes Used?
These cranes are the workhorses of industries that move massive, bulky, or high-value items:
Steel Mills & Metal Fabrication: Handling steel coils, sheets, plates, and fabricated structures.
Power Generation: Installing and maintaining turbines, generators, and transformers.
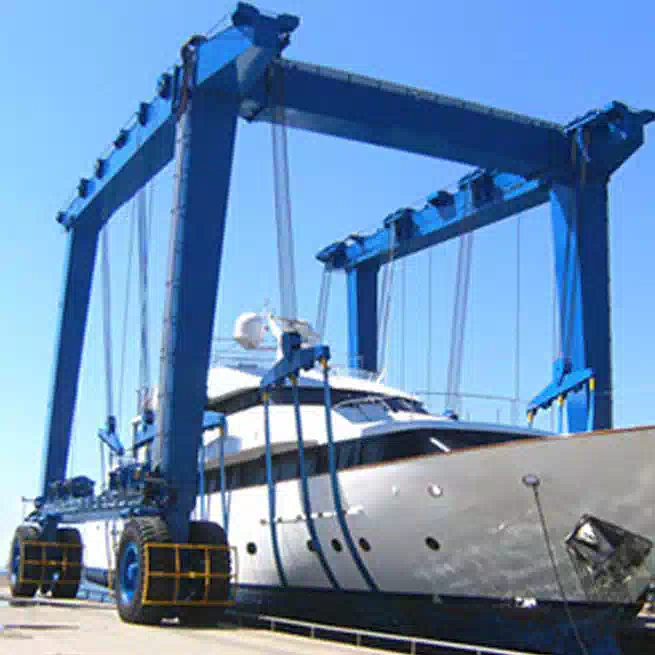
Shipbuilding & Offshore: Moving large ship sections, engines, and offshore modules.
Heavy Machinery Manufacturing: Assembling large mining equipment, presses, and industrial machinery.
Aerospace: Lifting aircraft components and assemblies.
Construction: Pre-cast concrete handling and positioning large structural elements.
Logistics & Intermodal Yards: Loading and unloading heavy containers and cargo.
Choosing the Right Double Girder Gantry Crane: Critical Specifications
Selecting the correct crane requires a detailed analysis of your operational needs:
Lifting Capacity (Tonnage): Determine the maximum weight to be lifted, including the weight of any lifting attachments. Always include a safety margin for future needs.
Span: The horizontal distance between the inside edges of the runway rails. This defines the crane's coverage area.
Lift Height: The required vertical travel distance of the hook from its highest to its lowest position.
Duty Cycle (FEM/ISO Classification): Assess how intensively the crane will be used (e.g., occasional use vs. continuous, heavy-duty cycling). This classification (like A5, A6, A7) affects motor sizing, braking, and structural design.
Mobility & Runway: Decide between a fixed-position gantry (permanently installed) or a mobile gantry (with rubber tires or wheels for relocation around a site).
Control & Safety Features: Options include:
Pendant control, cabin control, or radio remote control for flexibility and operator safety.
Essential safety devices: overload limiters, anti-collision systems, emergency stops, and wind sensors for outdoor cranes.
Environmental Conditions: Will the crane operate indoors, outdoors, in corrosive environments (e.g., chemical plants, marine climates), or in extreme temperatures? This dictates protection levels (IP ratings), paints, and special coatings.
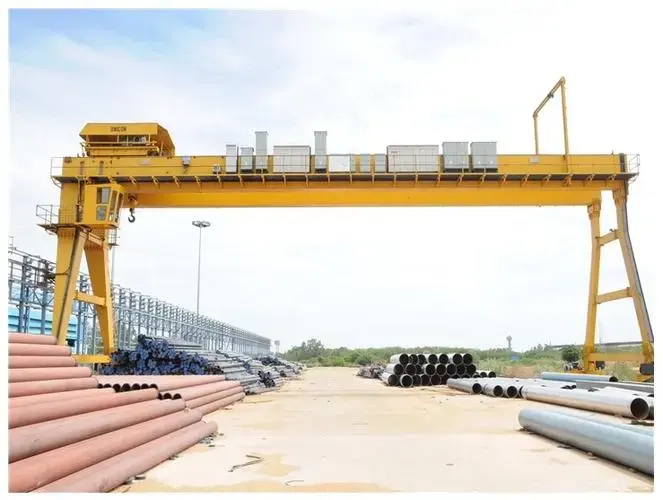

Technological Advancements & Smart Features
Modern double girder gantry cranes are becoming smarter and more connected:
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Ensure smooth acceleration and deceleration, enabling precise load positioning and reducing mechanical stress.
Condition Monitoring & IoT Sensors: Real-time monitoring of parameters like motor temperature, brake wear, and load weight allows for predictive maintenance, preventing unexpected downtime.
Automation & Integration: Cranes can be integrated into automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) or synchronized for tandem lifts, controlled by central warehouse management systems (WMS).
Conclusion
The double girder gantry crane is an indispensable engineering solution for heavy lifting where capacity, height, and reliability are paramount. Its robust design offers a compelling blend of power, precision, and adaptability that single girder cranes cannot match for the most severe applications.
Investing in a properly specified double girder gantry crane is an investment in long-term operational efficiency, safety, and productivity. By carefully evaluating your capacity, span, duty cycle, and operational environment—and partnering with a reputable manufacturer—you can secure a lifting solution that will serve as a reliable powerhouse for decades to come.
HI! Parter
Regarding your actual requirements, are you still unsure about which suitable crane to choose? Please contact our professional team immediately forfree consultation and personalized quotations. We will provide you with professional services and select the most suitable crane for you to optimize your operations, ensuring safety, efficiency and high productivity.
GET IN TOUCH
sale@nucleoncranes.global
https://ncranes.com
Tel
+86-17525962783