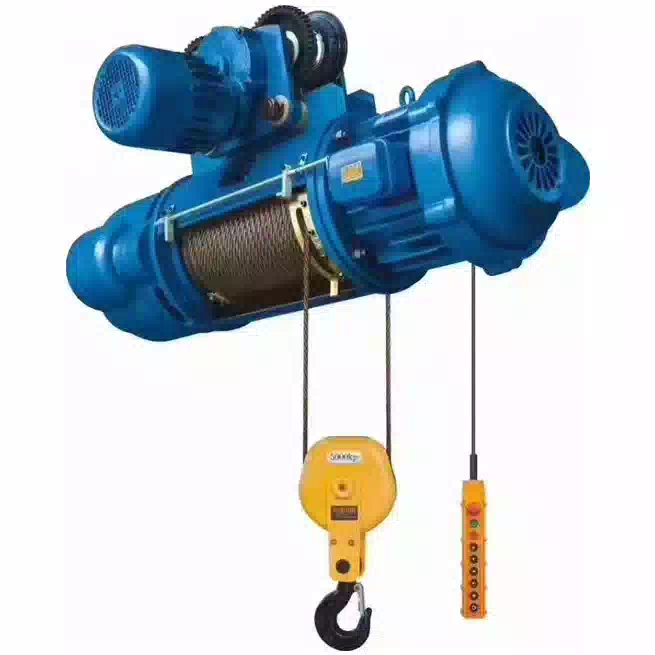
Introduction
In material handling and heavy lifting, efficiency and safety are paramount. Two of powerful workhorses in this industry are the Bridge Crane and the Gantry Crane. While they might seem similar at a glance, they serve distinct purposes and are suited for different environments. Choosing the wrong one can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs. This article will provide a clear comparison, exploring the difference between bridge crane and gantry crane, their basic components, how to select the right one, and their specific advantages and applications.
What is the Difference Between a Bridge Crane and a Gantry Crane?
The core difference between a bridge crane and a gantry crane lies in their support structure and mobility.
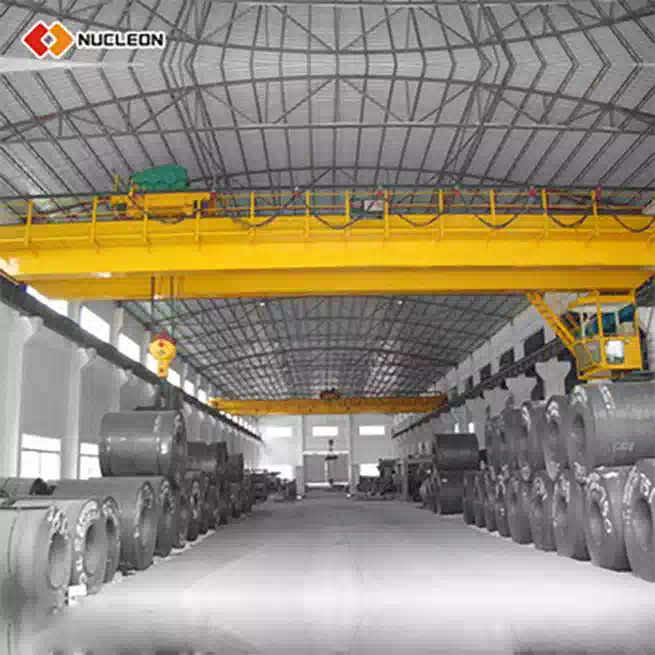
Bridge Crane (Overhead Crane): A bridge crane operates overhead, typically within a fixed building structure. Its runway is attached to the building's ceiling or supporting columns. The crane moves along these fixed runways, covering a precise, rectangular area on the floor below. It does not use floor space for its support.
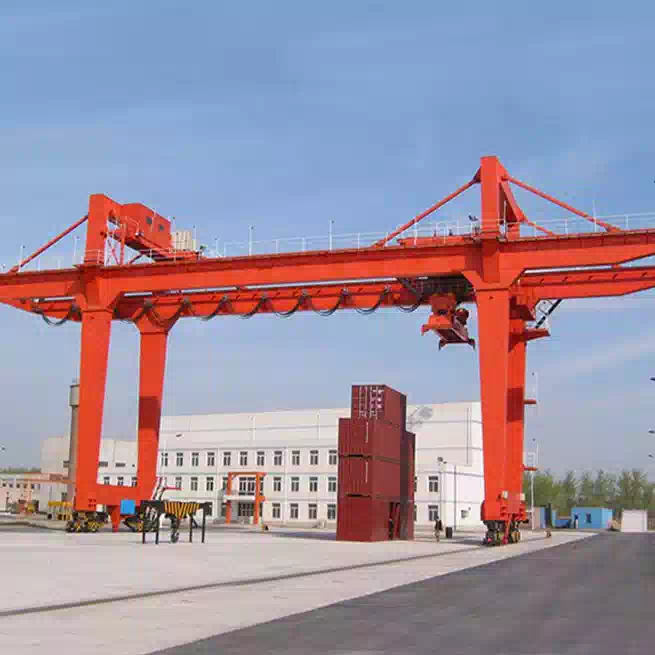
Gantry Crane: A gantry crane is a freestanding structure. It is supported by legs that run on fixed or mobile rails embedded in the floor (or on the ground).
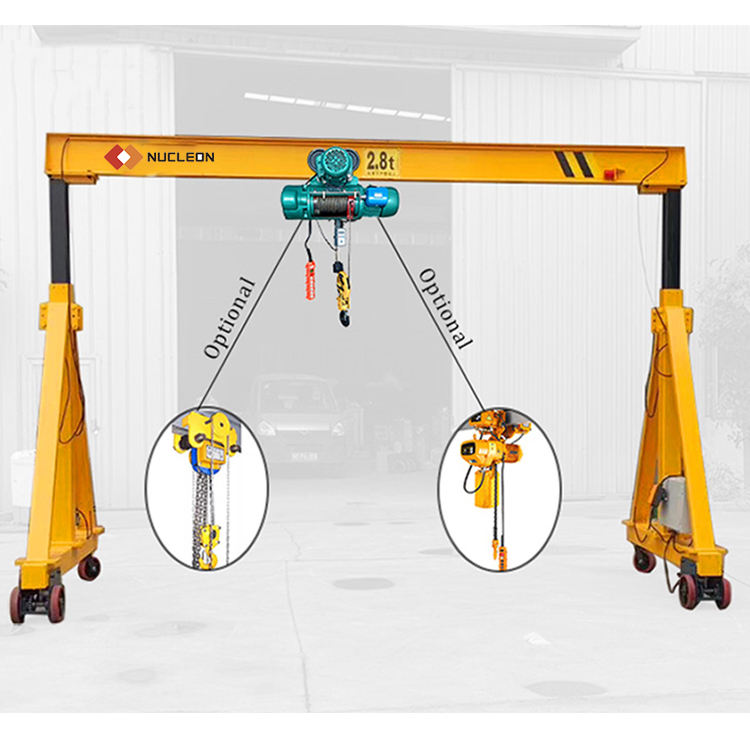

Gantry Crane
Basic Components of Bridge Cranes and Gantry Cranes
Despite their differences, both cranes share similar core components that enable their lifting functions.
Common Core Components:
Hoist: The primary lifting mechanism that raises and lowers the load.
Trolley: The unit that carries the hoist and moves laterally across the bridge/girder.
Bridge/Girder: The main horizontal beam that spans the work area. The trolley travels on this.
End Trucks: Located at each end of the bridge, they house the wheels that allow the crane to travel longitudinally.
Controls: Can be pendant (hanging) stations, radio remote controls, or operator cabins.
Unique Structural Components:
Bridge Crane Components: Includes runway beams fixed to the building structure for the end trucks to travel on.
Gantry Crane Components: Features legs that support the girder and wheels at the base of the legs for ground-level movement.
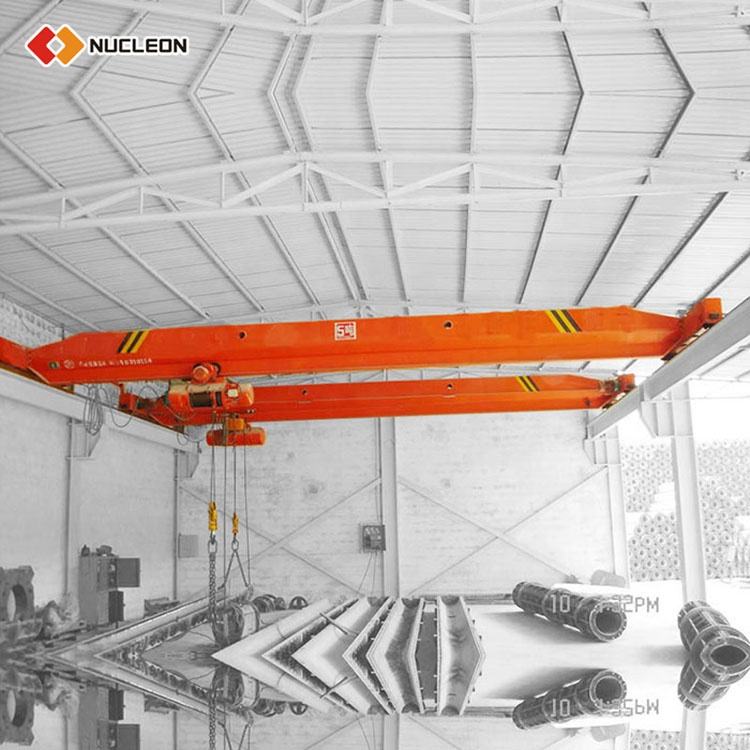

Overhead Crane
How to Choose: Bridge Crane or Gantry Crane?
The selection between a bridge crane and a gantry crane depends heavily on your facility and operational needs. Here are the key factors for crane selection:
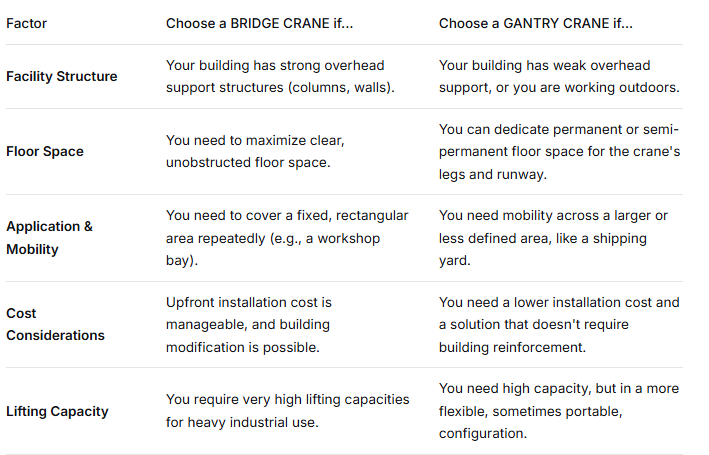
Advantages, Features, and Functions
Both cranes offer significant advantages in safety and efficiency over traditional forklifts or manual labor.
Bridge Crane Advantages & Features:
Floor Space: Since it’s overhead, it doesn't obstruct floor-level workflows.
High Lifting Capacity: Ideal for extremely heavy loads in manufacturing and steel handling.
Precision and Control: Offers smooth and precise load positioning over a defined area.
Durability and Integration: Built for heavy-duty, continuous cycles in an integrated facility.
Gantry Crane Advantages & Features:
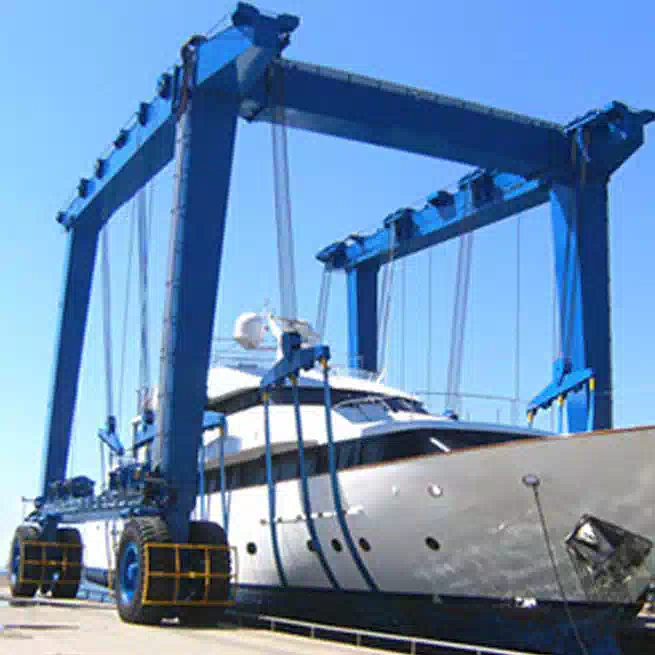
Versatility and Portability: Many gantry cranes are portable and can be relocated. No fixed infrastructure is needed.
Ideal for Outdoor Use: Perfect for shipbuilding, construction sites, and port operations.
Lower Installation Cost: Avoids the cost of reinforcing a building structure.
Flexibility: Can be designed with adjustable span and height to suit various applications.
Applicable Scenarios and Use Cases
Understanding the applicable scenarios for each crane is crucial for optimal deployment.
Bridge Crane Applications (Typically Indoors):
Manufacturing Workshops: Moving raw materials and finished products between assembly stations.
Warehouses and Distribution Centers: For stacking and retrieving heavy pallets.
Steel Mills and Foundries: Handling molten metal, coils, and heavy molds.
Power Plants: For maintenance and replacement of large generators and turbines.
Automotive Industry: Lifting vehicle chassis and heavy machinery.
Gantry Crane Applications (Often Outdoors or in Open Buildings):
Shipping Ports and Container Yards: The classic use for loading/unloading shipping containers from ships and trucks.
Shipbuilding and Repair: For moving large ship sections and components.
Construction Sites: Lifting pre-cast concrete panels, steel beams, and other materials.
Railway Yards: For maintenance and handling of locomotives and rail cars.
Large Outdoor Storage Areas: Moving heavy machinery and equipment
HI! Parter
Regarding your actual requirements, are you still unsure about which suitable overhead crane to choose? Please contact our professional team immediately forfree consultation and personalized quotations. We will provide you with professional services and select the most suitable electric overhead crane for you to optimize your operations, ensuring safety, efficiency and high productivity.
GET IN TOUCH
sale@nucleoncranes.global
Tel
+86-17525962783